
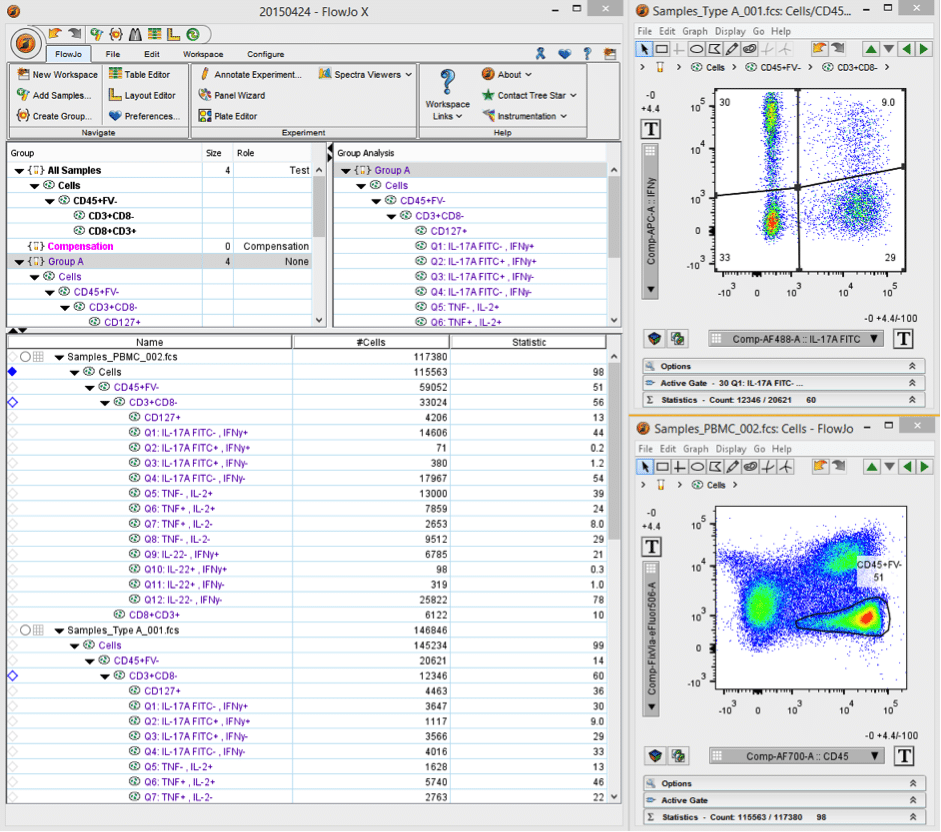
However, the true potential of flow cytometry methods for assessing target cell death has not been fully exploited. Numerous iterations of this technique have been reported and in many instances these assays have compared favorably with the 51Cr-release assay ( 5- 10). In this way, the number of target cells actually being killed is directly assessed. The premise for CTL assays using this methodology is relatively simple, with target cells being discriminated from other cells by fluorescent labels and target cell death determined using fluorescent viability markers. Flow cytometry is a high-throughput platform that has the capacity to simultaneously measure 12 or more parameters based on cell light scatter and fluorescence properties at a single cell level. One emerging methodology that overcomes the limitations associated with the 51Cr-release assay is the use of flow cytometry-based techniques to detect target cell death. Despite this, there are several drawbacks to this technique, including its reliance on cell lines that can take up 51Cr high spontaneous release of 51Cr from cells over time its semiquantitative nature interassay variability the requirement to often restimulate CTLs prior to the assay its biohazardous nature and its inability to directly assess cell killing in vivo.
In a testament to its efficacy, the 51Cr-release assay has remained the “gold standard” method for measuring CTL activity after more than five decades since its inception ( 4). Several methods have been developed to measure CTL cytotoxicity ( 3). The engagement of the TCR and the peptide/MHC-I complex results in CTL killing of the antigen-presenting cell, either through exocytosis of lytic granules towards the engaged target cell ( 1) or via expression of Fas ligand which ligates and multimerizes cognate death receptors on target cells ( 2). CTLs recognize target cells through interaction of their T-cell receptors (TCR) with “foreign” peptides presented by major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) molecules on target cells. Of particular interest in many immunotherapy protocols is the analysis of CD8 + cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL)-mediated killing of virus-infected cells and cancers cells. Sensitive methods for the measurement of an adaptive immune response are essential for the development of our understanding of the immune system and the development of immunotherapies.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
